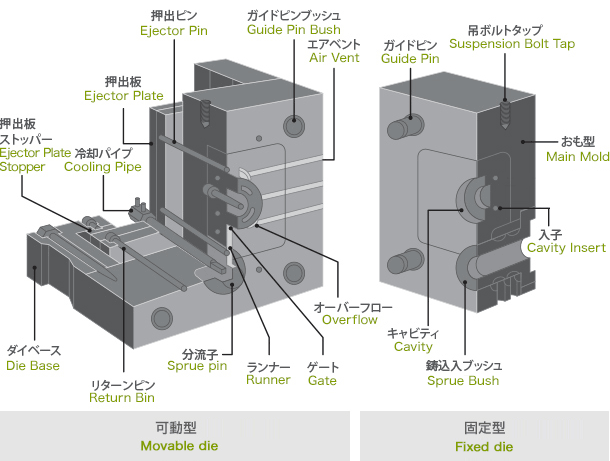
ダイカストマシンの作動状況
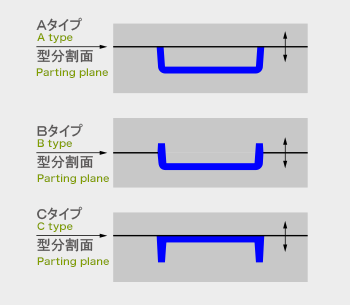
1つの形状でも、パーティングライン(A~C)のとり方はいろいろあります。
- 1. どんな合金を使用したら良いか。(使用条件による合金の性質を考慮する。)
- 2. 1型の中に多数の製品を彫りこめるか。(同形多数個取り、異形多数個取り)
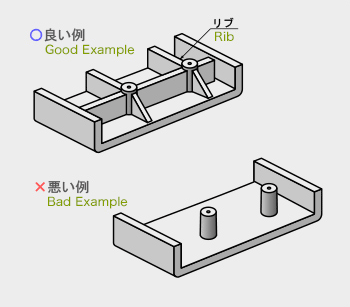
- 3. 金型の固定型、可動型の分割面をどこにするのか、いかに単純にできるか。
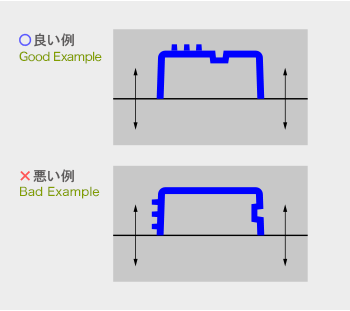
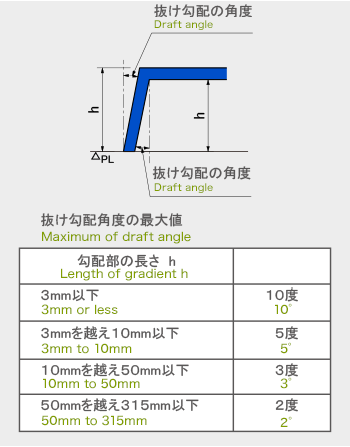
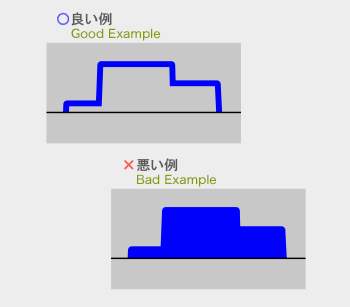
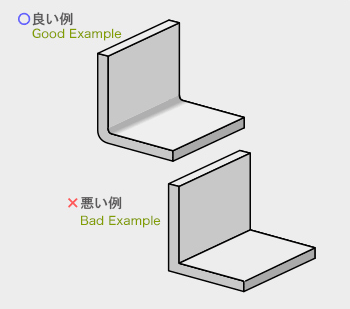
分割面の決定は寸法精度、抜勾配、湯流れ性、離型性、外観品質、内部巣の発生、
鋳バリ取り作業性、金型の寿命に大きな影響があり、重要な項目です。
Die Casting Machine Operating State
There are a variety of ways to get parting lines (A to C) even with a single form.
- 1. What alloy should be used? (Consider alloy properties depending on intended purpose.)
- 2. Can multiple products be carved into a single mold? (Multiples of identical shapes, or multiple different shapes)
- 3. Where put fixed-die and parting side of movable mold dividing surface and how simple can they be made?
To decide the parting side is an important subject because it affects dimensional accuracy, fluidly, draft, mold release, quality of appearance, occurrence of internal pockets, burring, and the life of the mold.